Energy from Waste
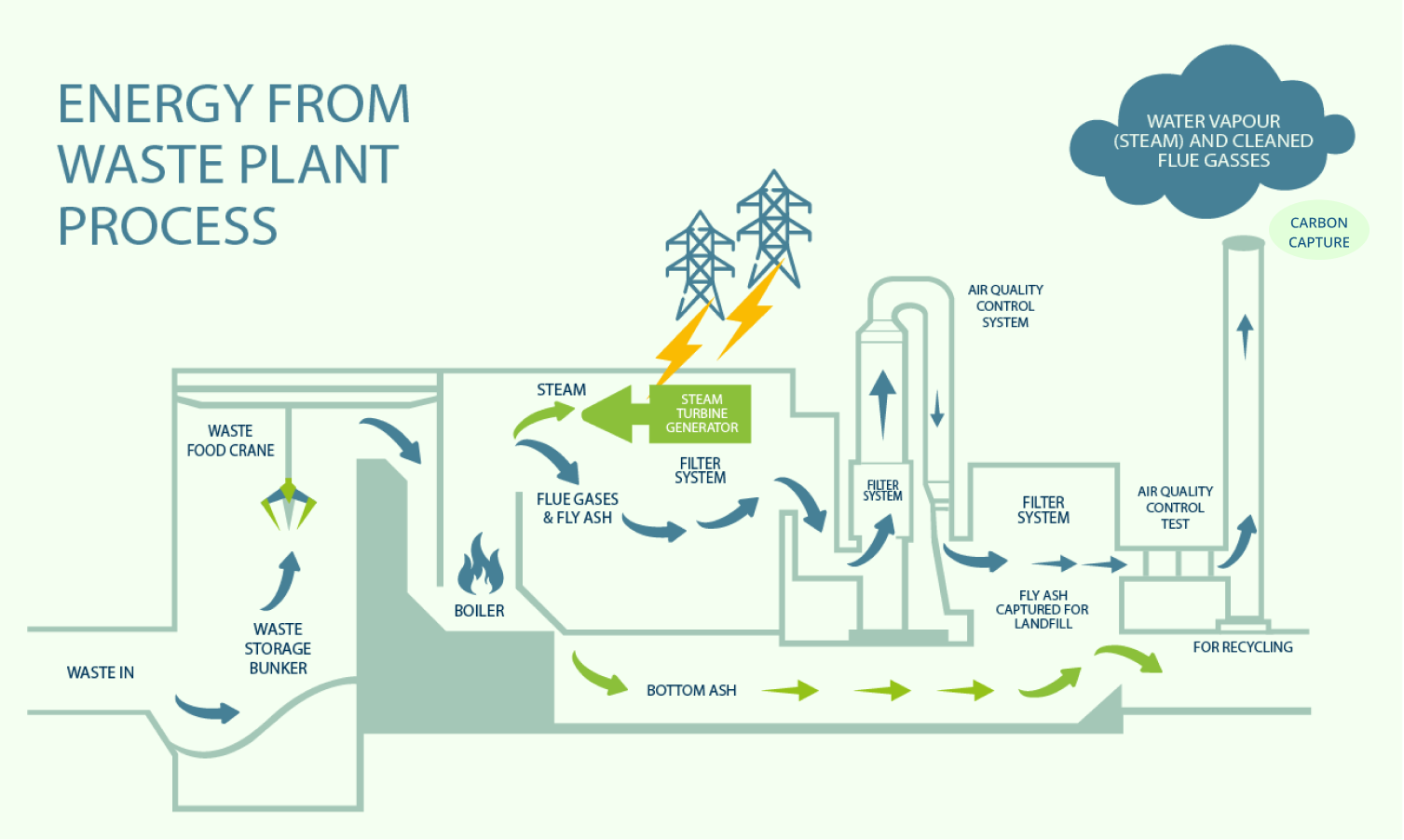
EfW produces energy from non-recyclable waste through processes like combustion, gasification and pyrolization. EfW plants transform this waste into energy used for electricity generation, for heating and cooling and for various industrial applications. Waste management is a key area for the sustainable preservation and development of our planet.
Worldwide, waste generation is expected to grow by roughly 60% by 2050 . Though EFW has been in practice for decades, newer and more advanced technologies are making the processes more viable. Waste management is turning into an integrated waste and resource management industry where non-recyclable waste is turned into a valuable resource for meaningful reuse. The EfW industry addresses the residual fraction of waste, which is waste of poor quality, waste that is rejected by recycling facilities, and polluted waste. This prevents the recycling cycle from the risk to be contaminated with polluted products and diverts the non-recyclable wate from landfills, dumpsites, and open fires. EFW is an important component of Sencirc’s footprint in a sensible circular future.
A compelling case for EfW plants globally

 EfW technologies treat non-recyclable waste: waste which is not fit for re-use or recycling and would otherwise be landfilled.
EfW technologies treat non-recyclable waste: waste which is not fit for re-use or recycling and would otherwise be landfilled. EfW Energy is a considerable sink for carbon dioxide (CO2) emissions: The diversion of waste from landfills prevents the production of methane emissions, which is up to 84 times more potent than CO2 over a 20-year period.
EfW Energy is a considerable sink for carbon dioxide (CO2) emissions: The diversion of waste from landfills prevents the production of methane emissions, which is up to 84 times more potent than CO2 over a 20-year period. EfW plants will increasingly contribute to low-carbon energy systems and circular societies : Thanks to advancing technologies, they will capture CO2, recover raw materials and supply more energy to decarbonise other sectors.
EfW plants will increasingly contribute to low-carbon energy systems and circular societies : Thanks to advancing technologies, they will capture CO2, recover raw materials and supply more energy to decarbonise other sectors.

The phasing out of polluting landfills is the first objective that should be pursued. Globally, 70% of the waste generated today is landfilled or openly dumped. The regulatory environment is varied when it comes to the EfW – while landfill bans and landfill taxes are an integral part of many economies, several other countries are yet to take a decisive action on landfills. However, there is only one way to go and that is an increasing number of energy from waste plants globally.
Portfolio